Solar panel connectivity refers to how solar panels are connected to form a solar power system. This connectivity can significantly impact the system’s overall performance and efficiency. The primary methods for connecting solar panels are series and parallel configurations. Each method has its benefits and drawbacks, which influence the effectiveness and reliability of a solar energy system.
Importance of Choosing the Right Connection
Choosing the right connection method is crucial as it affects the voltage, current, and overall performance of the solar power system. Understanding the differences between series and parallel connections can help you make an informed decision that optimizes energy production and system longevity.
2. Understanding Solar Panels
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They consist of multiple solar cells made from semiconductor materials, typically silicon. These cells generate direct current (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels work by utilizing the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the semiconductor material within the solar cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current. This DC electricity is then either used directly, stored in solar batteries, or converted to alternating current (AC) for use in household appliances through an inverter.
3. Series Connection
What is Series Connection?
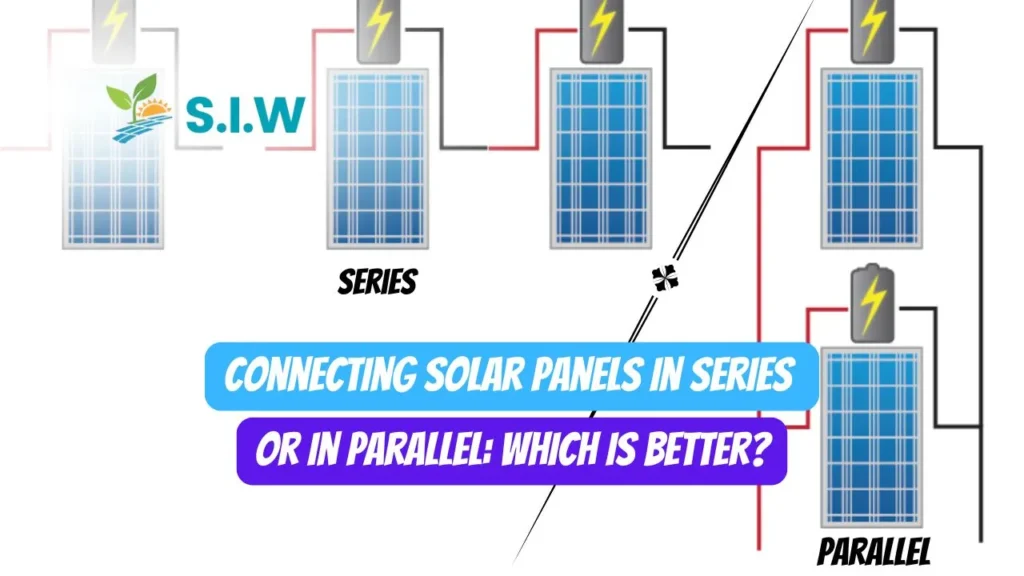
In a series connection, solar panels are connected end-to-end, meaning the positive terminal of one panel connects to the negative terminal of the next panel. This configuration increases the total voltage while keeping the current constant.
How Series Connection Affects Voltage and Current
When solar panels are connected in series, the voltage of each panel adds up while the current remains the same. For example, if each panel produces 30 volts and 8 amps, three panels in series will produce 90 volts and 8 amps. This increased voltage can be advantageous for long-distance transmission but may limit the current carrying capacity.
Advantages of Series Connection
- Increased Voltage: Ideal for systems that require higher voltage for efficient transmission.
- Simpler Wiring: Fewer wires are needed compared to parallel connections.
- Efficient for High Voltage Systems: Suitable for grid-tied systems requiring high voltage DC input.
Disadvantages of Series Connection
- Reduced Current Capacity: The system’s current is limited to the current rating of the individual panels.
- Impact of Shading: If one panel in the series is shaded or malfunctioning, it can reduce the performance of the entire string.
4. Parallel Connection
What is Parallel Connection?
In a parallel connection, solar panels are connected with all positive terminals linked together and all negative terminals linked together. This configuration increases the total current while keeping the voltage constant.
How Parallel Connection Affects Voltage and Current
When solar panels are connected in parallel, the current of each panel adds up while the voltage remains the same. For instance, if each panel produces 30 volts and 8 amps, three panels in parallel will produce 30 volts and 24 amps. This increased current is beneficial for systems that require higher current but limited voltage.
Advantages of Parallel Connection
- Increased Current Capacity: Suitable for systems that need higher current.
- Better Performance in Partial Shading: If one panel is shaded, the other panels can continue to operate efficiently.
- Flexibility: Easier to expand and modify the system.
Disadvantages of Parallel Connection
- Increased Wiring: More wires are needed compared to series connections.
- Potential for Higher Power Losses: Requires careful management to avoid losses due to resistance in wiring.
5. Comparing Series and Parallel
Efficiency and Performance
The choice between series and parallel connections affects the efficiency and performance of the solar power system. Series connections can be more efficient for high voltage applications, while parallel connections are better for high current scenarios.
Impact on System Voltage and Current
Series connections are best for applications requiring higher voltage, while parallel connections are suited for higher current requirements. Understanding the voltage and current needs of your system helps determine the most effective connection method.
Cost and Complexity
Series connections generally involve simpler wiring but may require higher voltage components. Parallel connections, while more complex in wiring, offer more flexibility and better performance in shaded conditions.
Suitability for Different Installations
The choice between series and parallel depends on the specific needs of the installation, such as the desired voltage and current, and the physical layout of the panels.
6. Expert Insights and Case Studies
Insights from Solar Energy Experts
Experts often recommend series connections for larger installations requiring higher voltage and parallel connections for residential systems needing higher current. Consulting with a solar energy professional can help tailor the connection method to your specific needs.
Case Studies of Series vs. Parallel Connections
Case studies demonstrate that series connections are effective in large-scale commercial solar panels installation where high voltage is required, while parallel connections are often preferred in residential systems due to their flexibility and performance in varying conditions.
7. Practical Applications and Future Trends
Best Practices for Solar Panel Connectivity
Choosing the right connection method involves considering factors like system voltage, current requirements, and shading conditions. Regular maintenance and monitoring are also essential to ensure optimal performance.
Emerging Trends in Solar Panel Technology
Advancements in solar technology, such as more efficient panels and smart grid integration, continue to evolve. These trends influence the optimal connection methods and overall system design.
8. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Both series and parallel connections have their advantages and disadvantages. Series connections offer higher voltage and simpler wiring, while parallel connections provide higher current capacity and better performance in shaded conditions.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Selecting the appropriate connection method depends on your specific needs and system requirements. Consulting with experts and considering future trends can help make an informed decision that maximizes the efficiency and longevity of your solar power system.